Terminus Group's Breakthrough in RIS-Assisted Wireless Security Published in Top-Tier Academic Journal
Terminus Group, in collaboration with researchers from the Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, has achieved a significant milestone in wireless communication security. Their groundbreaking work, titled “Can We Improve Channel Reciprocity via Loop-back Compensation for RIS-assisted Physical Layer Key Generation” has been accepted by a leading academic journal in signal processing, highlighting Terminus Group’s pioneering role in next-generation security solutions.
Research Highlights
The study addresses critical challenges in physical layer key generation (PKG), a lightweight encryption method essential for Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G/6G networks. While reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) enhance PKG by customizing wireless environments, they are vulnerable to jamming attacks and hardware interference, which degrade channel reciprocity — the foundation of symmetric key generation. Terminus Group’s proposed LoCKey scheme introduces a novel loop-back compensation mechanism combined with a minimum mean square error (MMSE) predictor to mitigate these issues. By enabling real-time calibration of channel state information (CSI) across multiple frequency bands, LoCKey significantly improves the consistency and security of key generation.
Experimental results demonstrate remarkable improvements:
Enhanced Correlation: LoCKey boosts CSI correlation coefficients by up to 40% compared to non-loop-back and traditional loop-back methods, even under aggressive RIS jamming attacks.
Higher Key Generation Rate (KGR): The scheme increases KGR by over 70% in low-SNR scenarios, leveraging RIS-induced randomness while countering interference.
Improved Key Consistency: The key disagreement rate (KDR) is reduced by 30%, ensuring reliable secure communication in dynamic environments.
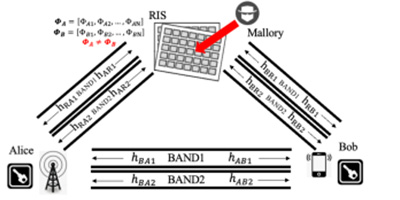
Fig. 1: RIS-assisted PKG system model with attacked RIS.
Industry Impact and Value
This research positions Terminus Group at the forefront of practical RIS applications for cybersecurity. By resolving reciprocity non-idealities without complex pre-coding or positional detection, LoCKey offers a scalable, cost-effective solution for mass IoT deployments, vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) networks, and mmWave systems. Its ability to harness RIS randomness while neutralizing attacks aligns with B5G/6G goals of endogenous security — reducing reliance on key pre-distribution and computational overhead.