Terminus Group's AI Breakthrough DREAM Model Accepted by AAAI-2025
Terminus Group, a leading global AIoT technology company, announced that its groundbreaking research paper "DREAM: Decoupled Discriminative Learning with Bigraph-aware Alignment for Semi-supervised 2D-3D Cross-modal Retrieval" has been accepted for publication at the Thirty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25), a premier academic conference. The research was conducted by a team led by Dr. Xian-Sheng Hua, CTO of Terminus Group, in collaboration with researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles, and other institutions.
This pioneering work tackles a critical challenge in artificial intelligence: efficiently retrieving relevant 3D data using 2D image queries (and vice-versa) with minimal human supervision. In real-world applications, obtaining vast amounts of accurately labeled 3D data is prohibitively expensive and time-consuming. The proposed DREAM framework directly addresses this "label scarcity" problem and the significant "heterogeneous gap" between 2D and 3D modalities.
The core innovation of DREAM lies in its novel "learning-to-selectively-learn" perspective. It decouples the processes of label prediction and reliability measurement to reduce overconfident pseudo-labels — a common pitfall in semi-supervised learning. Specifically, DREAM features a propagation-enhanced label prediction module for accurate pseudo-labeling and a unique, learnable reliability measurement module that scores the confidence of these predictions. High-quality samples are selected for training using adaptive class-specific thresholds. Furthermore, the model intelligently utilizes less reliable data through a "multimodal negative learning" technique, which provides soft supervision by identifying improbable labels. To bridge the modality gap, DREAM introduces a "bigraph-aware modality alignment" strategy, constructing a bipartite graph to connect similar cross-modal examples and effectively aligning their semantic representations in a shared space.
Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets like ModelNet10 and ModelNet40 demonstrate DREAM's superiority, consistently outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods in retrieval accuracy.
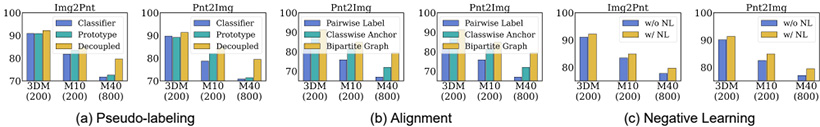
Figure 4: Ablation study on(a) pseudo-labeling techniques,(b) alignment strategies,(c) the negative learning module.
This research holds significant value for industries reliant on 3D visual data, such as autonomous driving, robotics, augmented/virtual reality, and e-commerce, etc. By dramatically reducing the dependency on labeled data, DREAM lowers the barrier for developing sophisticated cross-modal retrieval systems. It enables more seamless integration between the vast amount of existing 2D visual content and the growing ecosystem of 3D models, paving the way for more intelligent and intuitive human-computer interactions. The acceptance of this paper at AAAI-25 underscores Terminus Group's commitment to advancing the frontiers of AI research and its capability to deliver impactful technological innovations.