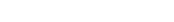Terminus Group Achieves New Breakthrough in Spatial Intelligence R&D, Enabling Dynamic High-Dimensional Perception
Recently, Dr. Ling Shao, Chief Scientist and International President of Terminus, together with his research collaborators, released their latest achievements by introducing a novel second-order anchor technique for enhancing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS), termed SOGS (Second-Order Gaussian Splatting). This advancement holds significant application potential across spatial intelligence domains such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), autonomous driving, robotic navigation, as well as film and game production. The research has been accepted by CVPR 2025, one of the most prestigious conferences in the field of artificial intelligence, under the title: SOGS: Second-Order Anchor for Advanced 3D Gaussian Splatting.

The proposed SOGS method enables simultaneous rendering of high-quality textures and geometric structures while substantially reducing model size. Figures (a) and (b) respectively show rendered images and gradient maps generated by Scaffold-GS and SOGS using the "Stump" and "Room" samples from the Mip-NeRF360 dataset. The gradient maps, extracted via the Sobel operator, highlight the textural and geometric features of the scenes.
SOGS effectively addresses several key challenges in 3D-GS: the trade-off between anchor feature dimensions and model size, the loss of local texture and structural detail, and imbalances in rendering optimization. As such, it demonstrates broad application potential in multiple spatial intelligence scenarios:
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): Real-time rendering boosts frame rates in VR/AR headsets, reducing motion sickness risk. The lightweight model adapts to devices such as smartphones and tablets, enabling high-quality real-time scene overlays.
Autonomous Driving and Robotic Navigation: Builds 3D models of roads and obstacles from sparse views to support decision-making; integrates LiDAR and other sensor data to create compact 3D Gaussian representations, improving environmental perception efficiency.
Film and Game Production: Serves as an alternative to traditional NeRF methods, accelerating real-time preview and VFX production of complex movie scenes. Anchor compression reduces memory requirements for game environments while preserving details such as vegetation textures and architectural structures.
Urban Planning and Architectural Modeling: Enables rapid generation of high-fidelity city models, supporting applications such as traffic flow simulation and urban planning.
...
Excerpt from the paper:
Anchor-based 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) leverages anchor features in Gaussian prediction to reduce redundancy while achieving impressive 3D rendering quality. However, it often faces a trade-off between anchor feature dimensions, model size, and rendering quality—larger anchor features lead to bigger models and higher-quality rendering, while smaller features degrade Gaussian attribute prediction, introducing artifacts in texture and geometry.
To address this, the team designed SOGS, an anchor-based 3D-GS method that introduces second-order anchors to achieve both superior rendering quality and reduced feature dimensions/model size. Specifically, SOGS incorporates covariance-based second-order statistics and feature correlation to enhance per-anchor representation, compensating for reduced feature size while improving rendering quality. Additionally, a selective gradient loss is introduced to strengthen optimization of scene textures and geometries, thereby enabling high-quality rendering even with compact feature dimensions.
Extensive experiments across widely adopted benchmark datasets demonstrate that SOGS significantly improves rendering quality for novel view synthesis tasks while drastically reducing model size.